For example you can use this console logger in your JDeveloper 11g application. It opens automatically when you start your web application.

To activate this just add these context parameters to your web.xml

package nl.whitehorses.esb.xslt.functions.headers;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StringWriter;
import oracle.tip.esb.server.headers.ESBHeaderContext;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import oracle.xml.parser.v2.XMLDocument;
public class ESBCustomFunctions {
public static String getHeader() throws IOException {
Element requestHeader = ESBHeaderContext.getRequestHeader();
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(sw);
((XMLDocument)requestHeader.getOwnerDocument()).print(pw);
return sw.toString();
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<extension-functions>
<functions xmlns:customESBFunctions="http://www.oracle.com/XSL/Transform/java/nl.whitehorses.esb.xslt.functions.headers.ESBCustomFunctions">
<function name="customESBFunctions:getHeader" as="string">
</function>
</functions>
</extension-functions>
 When we open a XSLT file, we can see our function in the component palette. Just drag this function in the editor
When we open a XSLT file, we can see our function in the component palette. Just drag this function in the editor JDeveloper will automatically add the namespace to the xslt
JDeveloper will automatically add the namespace to the xslt Because this getHeader function give me the escaped soap header back, Let's transform this to xml with a litte help of the parseEscapedXML function.
Because this getHeader function give me the escaped soap header back, Let's transform this to xml with a litte help of the parseEscapedXML function. Now we only have to put our jar with our getHeader function on the soa suite server. Put the jar in the applib folder of the soa suite container. Last step is to add the jar to the system.xml of the soa suite container. Add the jar to the oracle.bpel.common shared library entry.
Now we only have to put our jar with our getHeader function on the soa suite server. Put the jar in the applib folder of the soa suite container. Last step is to add the jar to the system.xml of the soa suite container. Add the jar to the oracle.bpel.common shared library entry.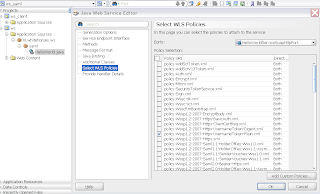 The Helloworld Web Service with HTTPS and plain username policy which I use in this example.
The Helloworld Web Service with HTTPS and plain username policy which I use in this example.
package nl.whitehorses.ws.saml;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import weblogic.jws.Policy;
@WebService(name = "HelloWorldService", portName = "HelloWorldServiceSoapHttpPort")
@Policy(uri = "policy:Wssp1.2-2007-Https-UsernameToken-Plain.xml")
public class HelloWorld {
public HelloWorld() {
}
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello world";
}
}
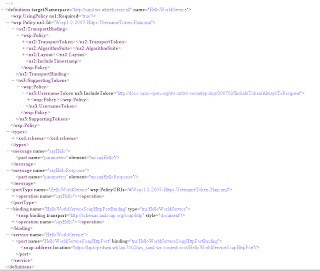 Save this xml to the HelloworldService.wsdl file and open this in a editor. We have to remove the policy reference in the porttype and add this to the binding
Save this xml to the HelloworldService.wsdl file and open this in a editor. We have to remove the policy reference in the porttype and add this to the binding
<portType name="HelloWorldService" wsp:PolicyURIs="#Wssp1.2-2007-Https-UsernameToken-Plain.xml">
<operation name="sayHello">
<input message="tns:sayHello"/>
<output message="tns:sayHelloResponse"/>
</operation>
</portType>
<binding name="HelloWorldServiceSoapHttpPortBinding" type="tns:HelloWorldService">
<soap:binding transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http" style="document"/>
<operation name="sayHello">
<soap:operation soapAction=""/>
<input>
<soap:body use="literal"/>
</input>
<output>
<soap:body use="literal"/>
</output>
</operation>
</binding>
<portType name="HelloWorldService">
<operation name="sayHello">
<input message="tns:sayHello" />
<output message="tns:sayHelloResponse" />
</operation>
</portType>
<binding name="HelloWorldServiceSoapHttpPortBinding" type="tns:HelloWorldService">
<ns2:PolicyReference xmlns:ns2="http://www.w3.org/ns/ws-policy" URI="#Wssp1.2-2007-Https-UsernameToken-Plain.xml"/>
<soap:binding transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http" style="document" />
<operation name="sayHello">
<soap:operation soapAction="" />
<input>
<soap:body use="literal" />
</input>
<output>
<soap:body use="literal" />
</output>
</operation>
</binding>
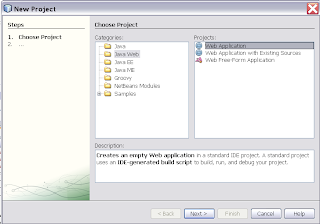 Select the new project and add a new Web Service Client
Select the new project and add a new Web Service Client Select the HelloworldService wsdl
Select the HelloworldService wsdl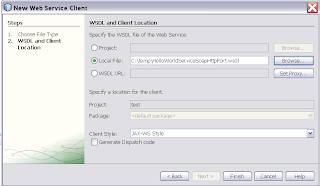 Select the just created web service reference and select "Edit Web Service Attributes" on this reference
Select the just created web service reference and select "Edit Web Service Attributes" on this reference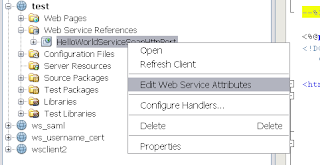 Deselect "Use development defaults" and provide a Username / password of a valid Weblogic account.
Deselect "Use development defaults" and provide a Username / password of a valid Weblogic account.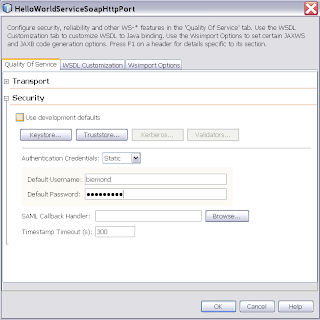 Select for the private key which will be used in the encryption.
Select for the private key which will be used in the encryption.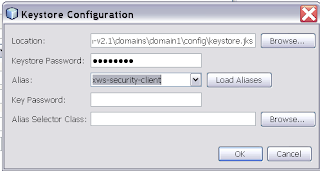
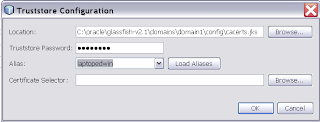 When we take a look at the META-INF folder in the source folder, we can see that the wizard has created a web service configuration file which will be used by Metro to setup the security to the Weblogic Web Service
When we take a look at the META-INF folder in the source folder, we can see that the wizard has created a web service configuration file which will be used by Metro to setup the security to the Weblogic Web Service To test this web service client, we will add a servlet to the project
To test this web service client, we will add a servlet to the project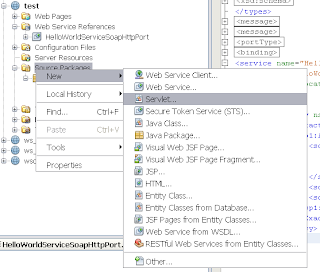
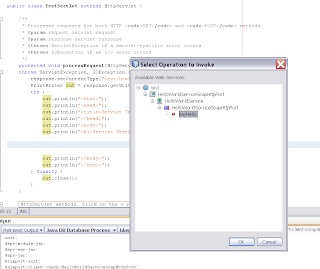 At the project properties we can call the servlet by using the servlet url in the relative url ( Run)
At the project properties we can call the servlet by using the servlet url in the relative url ( Run)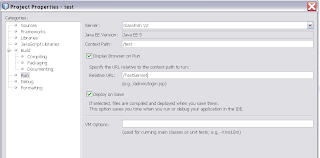 That's all , it should be working now. For more policies examples see this url , there are some nice examples about Secure Token Service STS.
That's all , it should be working now. For more policies examples see this url , there are some nice examples about Secure Token Service STS. Define the keystores, I have my own keystores but you can also use the WLS demo keystores
Define the keystores, I have my own keystores but you can also use the WLS demo keystores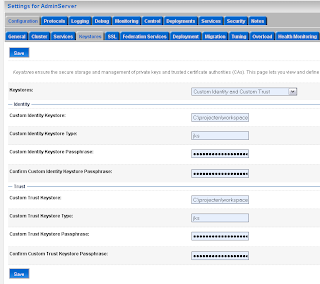
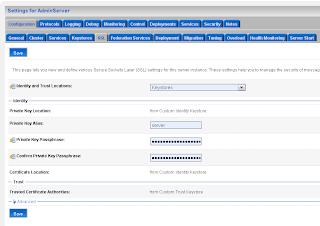 Add a SAML 1.1 source site at the Federation Services tab.
Add a SAML 1.1 source site at the Federation Services tab.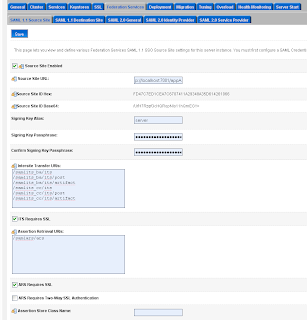 The second step on the SAML Source site is to configure the myrealm security domain. In this step we start by adding a Credential Mapping.
The second step on the SAML Source site is to configure the myrealm security domain. In this step we start by adding a Credential Mapping.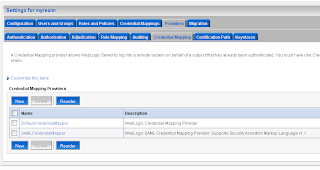 In the provider Specific Tab of the just created credential mapping we have to define the details.
In the provider Specific Tab of the just created credential mapping we have to define the details.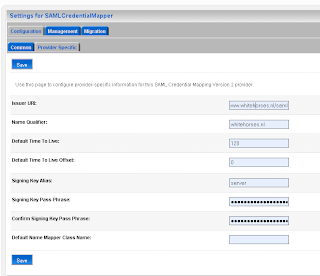
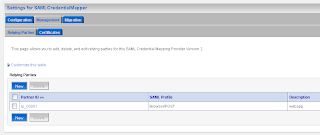 Add the url of secured page ( the url of the second application ) and the https port of the SAML destination url. Here we also have to provide the assertion id of the client SAML. This is APID=ap_00001. We will create this later (asserting party ) on the destination SAML domain.
Add the url of secured page ( the url of the second application ) and the https port of the SAML destination url. Here we also have to provide the assertion id of the client SAML. This is APID=ap_00001. We will create this later (asserting party ) on the destination SAML domain.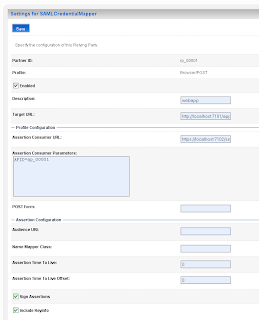 For the communication we need to import the public keys. In my case is this the ca and the server public key. Just export these key from the keystores and rename these keys to the der file extension.
For the communication we need to import the public keys. In my case is this the ca and the server public key. Just export these key from the keystores and rename these keys to the der file extension.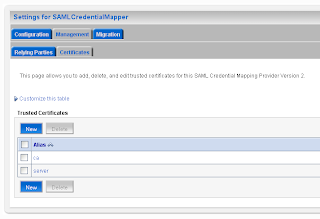
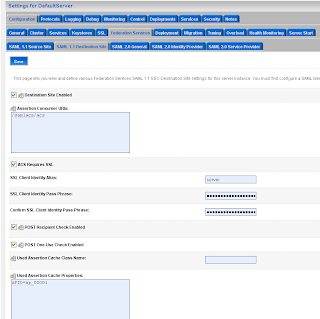 Go to the myrealm security domain and add a new SAML authentication.
Go to the myrealm security domain and add a new SAML authentication.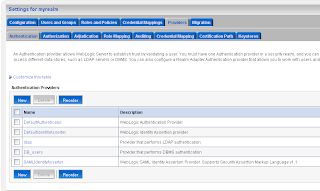 Add a new asserting party.
Add a new asserting party.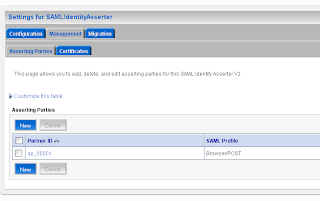 Here we add the url of the application which run on the source site. And the id of the relying party on the source site.
Here we add the url of the application which run on the source site. And the id of the relying party on the source site.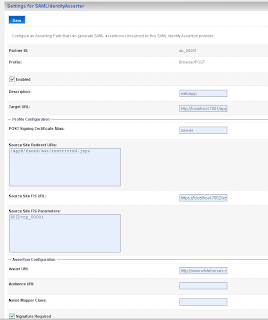 Here we also have to import the public keys of ca and server.
Here we also have to import the public keys of ca and server.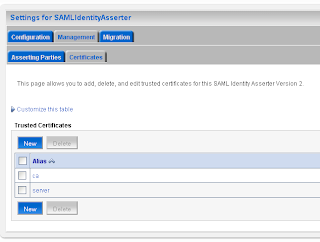 The last WebLogic step is to add a common authorization provider on both domains. I use a LDAP or a SQL authenticator for this. Both WLS domains need to have the same users and groups.
The last WebLogic step is to add a common authorization provider on both domains. I use a LDAP or a SQL authenticator for this. Both WLS domains need to have the same users and groups.
<security-constraint>
<web-resource-collection>
<web-resource-name>aut</web-resource-name>
<url-pattern>/faces/aut/*</url-pattern>
</web-resource-collection>
<auth-constraint>
<role-name>valid-users</role-name>
</auth-constraint>
</security-constraint>
<login-config>
<auth-method>BASIC</auth-method>
<realm-name>myrealm</realm-name>
</login-config>
<security-role>
<role-name>valid-users</role-name>
</security-role>
<?xml version = '1.0' encoding = 'windows-1252'?> <weblogic-web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.bea.com/ns/weblogic/weblogic-web-app.xsd" xmlns="http://www.bea.com/ns/weblogic/weblogic-web-app"> <security-role-assignment> <role-name>valid-users</role-name> <principal-name>users</principal-name> </security-role-assignment> </weblogic-web-app>
<security-constraint>
<web-resource-collection>
<web-resource-name>aut</web-resource-name>
<url-pattern>/faces/aut/*</url-pattern>
</web-resource-collection>
<auth-constraint>
<role-name>valid-users</role-name>
</auth-constraint>
</security-constraint>
<login-config>
<auth-method>CLIENT-CERT</auth-method>
<realm-name>myrealm</realm-name>
</login-config>
<security-role>
<role-name>valid-users</role-name>
</security-role>
 The same, with now JSON as output.
The same, with now JSON as output. Request for all the employees with xml as output
Request for all the employees with xml as output

 Now we are ready to start with the OSB. First create the Business services where we call the XMLdb servlets. Select any xml as input and http as transport. We need also to create a Service Account with the hr username / password and add this to the Business service.
Now we are ready to start with the OSB. First create the Business services where we call the XMLdb servlets. Select any xml as input and http as transport. We need also to create a Service Account with the hr username / password and add this to the Business service.



 In the request parameter we need to retrieve the request url and the parameters. To get the url we can use. $inbound/ctx:transport/ctx:request/http:relative-URI/text() and the get the requested output we can use $inbound/ctx:transport/ctx:request/http:query-string/text() . These parameters will be used by the java callout. In the response pipeline I will add a java callout.
In the request parameter we need to retrieve the request url and the parameters. To get the url we can use. $inbound/ctx:transport/ctx:request/http:relative-URI/text() and the get the requested output we can use $inbound/ctx:transport/ctx:request/http:query-string/text() . These parameters will be used by the java callout. In the response pipeline I will add a java callout.
private static void invoke(Object inst,Method m, JSONObject obj){
try {
m.invoke(inst, new Object[] { obj });
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static JSONArray convert(JSONArray json,String type) {
ListIterator list = json.listIterator();
Class dynamicConvertorClass = null;
Object clazzInst =null;
Method m = null;
try {
dynamicConvertorClass = Class.forName("nl.whitehorses.json.convertor."+type.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + type.substring(1).toLowerCase());
clazzInst = dynamicConvertorClass.newInstance();
m = dynamicConvertorClass.getMethod("changeType", new Class[] { JSONObject.class });
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
while ( list.hasNext() ) {
JSONObject obj = (JSONObject)list.next();
invoke (clazzInst,m,obj);
}
return json;
}
private static JSONObject convert(JSONObject json,String type) {
Class dynamicConvertorClass = null;
Object clazzInst =null;
Method m = null;
try {
dynamicConvertorClass = Class.forName("nl.whitehorses.json.convertor."+type.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + type.substring(1).toLowerCase());
clazzInst = dynamicConvertorClass.newInstance();
m = dynamicConvertorClass.getMethod("changeType", new Class[] { JSONObject.class });
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
invoke (clazzInst,m,json);
return json;
}
public static String xmlToJson(XmlObject xml, String type, String output)
{
if ( type.indexOf("/") > 0 ) {
type = type.substring(0,type.indexOf("/"));
}
System.out.println("type "+type);
System.out.println("content "+xml.xmlText());
if ( output.equalsIgnoreCase("output=json") ){
if ( !type.equalsIgnoreCase("not")) {
XMLSerializer ser = new XMLSerializer();
Object res = ser.read( xml.xmlText() );
if ( res instanceof JSONArray ) {
JSONArray json = (JSONArray) res;
json = convert(json,type);
return json.toString(1,0);
}
if ( res instanceof JSONObject ) {
JSONObject json = (JSONObject) res;
json = convert(json,type);
return json.toString(1,0);
}
}
}
return xml.xmlText();
}
public void changeType(JSONObject obj){
Object a = obj.get("SALARY");
if ( a!= null) {
obj.put("SALARY",new Float(a.toString()));
}
a = obj.get("EMPLOYEE_ID");
if ( a!= null) {
obj.put("EMPLOYEE_ID",new Float(a.toString()));
}
a = obj.get("MANAGER_ID");
if ( a!= null) {
obj.put("MANAGER_ID",new Float(a.toString()));
}
a = obj.get("DEPARTMENT_ID");
if ( a!= null) {
obj.put("DEPARTMENT_ID",new Float(a.toString()));
}
a = obj.get("HIRE_DATE");
SimpleDateFormat sdfInput = new SimpleDateFormat ("d-MMM-yy") ;
Date date = null;
try {
date = sdfInput.parse(a.toString());
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if ( a!= null) {
obj.put("HIRE_DATE",date);
}